Insulin resistance has become epidemic, with an estimated two-thirds of the population suffering from its symptoms. These symptoms include abdominal fat skin tags and sugar cravings. Untreated insulin after eating food can lead to type 2 diabetes and heart disease, where cells stop responding to insulin.
There are a bunch of unhealthy habits and factors that lead to insulin resistance. However, the prime reasons behind insulin resistance include obesity, chronic stress, unhealthy diet, sedentary routine lifestyle, PCOS, and high dose of steroids.
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin is a hormone that controls blood sugar and is made by an organ called the pancreas. The pancreas transmits insulin into your blood after consuming food or if it inspects the high blood sugar level in your body. So what is insulin resistance? After eating food, the body breaks it into usable energy called glucose. When your body cell stops responding to insulin, the body doesn’t process glucose how it naturally does. Hence, the sugar stays and starts to accumulate in your bloodstream. As a result, high blood sugar levels lead to diabetes.
Now that we know what insulin resistance is and how it is caused, this brings us down to the question: Can you reverse insulin resistance with diet? The answer is YES! You can overcome this health issue if considerable lifestyle changes are adapted to achieve good health – Most importantly, your diet. Insulin resistance diet is one of the main factors combined with physical activities, high protein, and a low sugar diet to lower the risk for insulin resistance.
Importance of Caloric Intake for Insulin Resistance Diet
According to Basic Science Investigation findings, calorie limitation helps patients to prevent further growth of insulin resistance. It is an elemental therapy for people with insulin resistance. Even people with obesity can lose weight by calorie restriction to avoid formulating diabetes.
Hence, one should know the calorie intake limit and expert recommendations to comply with the best health policies. The prescribed calorie intake guideline by the National Institute of Health (NIH) is as follow:
- 1,200 to 1,600 calories intake per day for small to medium-sized women. Physically active small women or medium-sized women who don’t exercise regularly.
- 1,600 to 2,000 calories per day for large women, small healthy men, or large men who want to lose weight is recommended.
- 2,000 to 2,400 caloric intake per day for physically active medium to large-size men and women is considerable.
Recommendations for Managing Diabetes
A healthy lifestyle for people with diabetes needs a balance with an insulin resistance diet and regular workout. American Diabetes Association has made some recommendations to prevent diabetes.
- People with a high risk of stimulating type 2 diabetes are recommended to include a caloric deficit diet and a low dietary fat intake. A moderate 7% body weight loss and an active routine of 150min/week workout can lower the risk of diabetes.
- Adjust insulin doses advised for a planned workout routine. For the patient with an unplanned workout, extra carbohydrate is recommended.
- Monitor healthy carbohydrates and taking carbs from vegetables, fruits, low-fat milk for better health results.
- Insulated with glucose-lowering treatments, sucrose-filled food can be a substitute for carbohydrates. Make sure not to take excess energy intake.
- By FDA, non-nutritive sweeteners are safe at a moderate level for daily intake, without going overboard.
Glycemic Index
Glycemic index is a measurement of food with carbohydrates. It ranks food according to their relative ability to how quickly blood sugar level rises after consuming them. Foods containing high GI numbers raise blood sugar levels rapidly, like processed carbs and sugar. Food having a low GI rate contains almost minimum to no carbs, which the body can not absorb quickly.
The purpose of knowing the glycemic index (GI) is to choose food with carbohydrates that do not increase blood sugar levels rapidly.
Low-GI: Food with 55% or less score like green vegetables, kidney beans, chickpeas, and lentils.
Medium-GI: Food with 59 to 60 percent score such as multigrain, whole wheat pita bread, oats, sweet corn, raisins, breakfast cereal.
High-GI: Food with 70% and above score russet potatoes, melon, white bread, and rice.
7 Healthy Meal Planning Tips
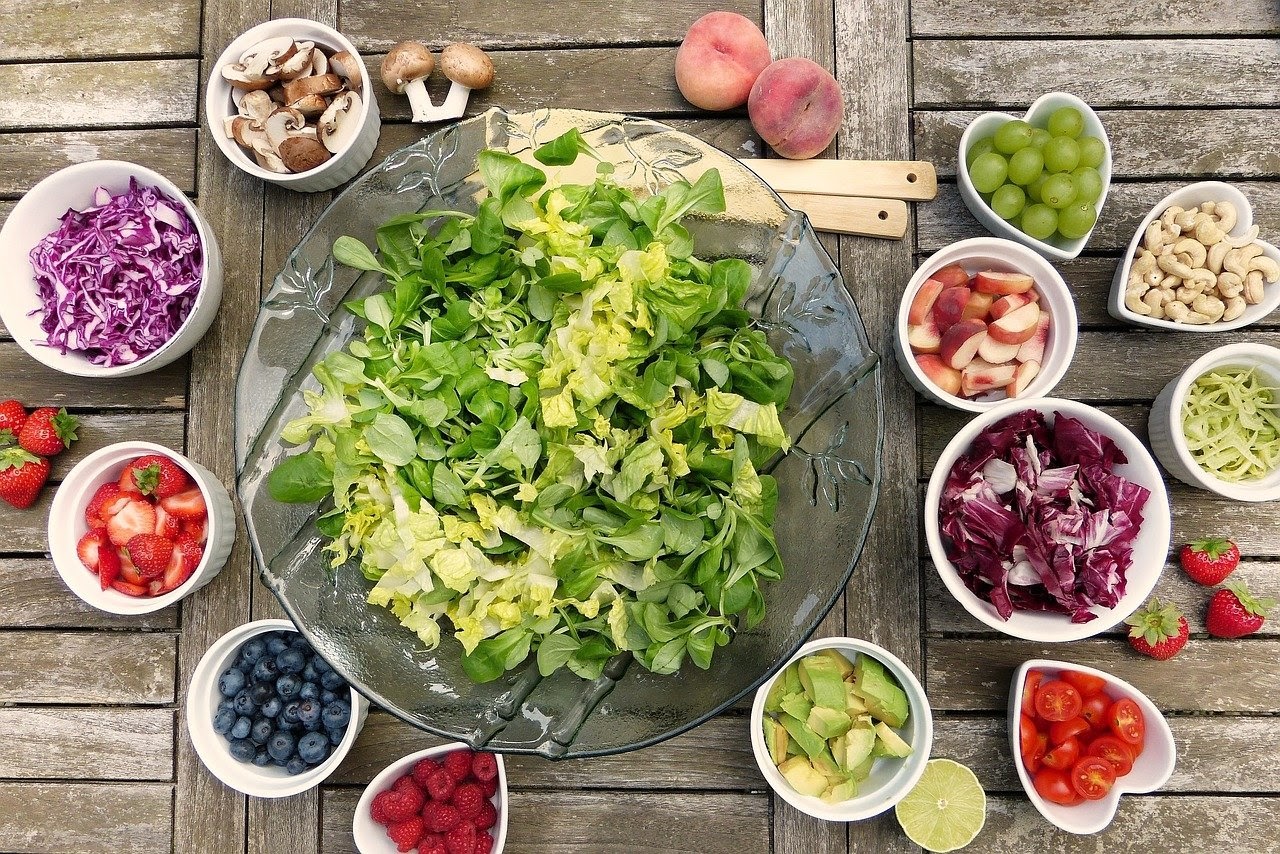
While making your shopping list for an insulin resistance diet, one should keep in mind the healthy but insulin-resistant food for your daily intake. Avoid eating sugar contained food, junk, processed items, and fried food. We have listed down what food should be in your insulin resistance diet menu to help you make better choices – Ultimately, achieving a healthy lifestyle.
Lots of Vegetables
We all are aware of the benefits of eating vegetables, but you should fill up your big part of the plate with lots of vegetables when it comes to insulin resistance. Raw and fresh vegetables are low in calories which makes you fuller for longer. Instead of focusing only on green vegetables, it is advised to eat a variety of them because they all contain different nutrients that benefit you one way or another.
Non Starchy vegetables are most suitable for controlling diabetes, such as:
- Asparagus
- Broccoli
- Kale
- Onion and tomato
- Mushroom
- Spinach
- Peppers
- Brussels sprouts
Healthy Fruits
Fruits are a great alternative for sugar cravings. Best of all, fruits have a low glycemic index, meaning they don’t raise blood sugar levels, unlike other sweeteners. Studies have found that a higher intake of fruits lowers the risk of type 2 diabetes.
The healthiest option of fruits for diabetic patients with insulin resistance are:
Oranges: A medium-sized orange contains 17 grams of carbohydrates.
Blackberries: One cup of raw berries has 14 grams of carbohydrates.
Strawberries: One cup of strawberries has 11 grams of carbohydrates.
Other Low GI rates include bananas, apples, mangoes, dates, and pears.
Good Fats
Contrary to popular opinion, fats are not bad for your health. What is important is selecting the fat that is healthy for your heart. Studies have found that a human’s saturated fat is prone to worsen insulin resistance. On the other hand, polyunsaturated and monounsaturated modification helps improve the cell membrane composition.
Even healthy fats like olive oil have 45 calories per teaspoon, so moderation is the key while using oils in your food. Mostly recommended fat options include 100 calories of nuts, avocado, fatty fish with an omega-3 fatty acid, and any oil in moderation of 1-2 teaspoon.
Whole Grain Food
Whole grains are not only healthy, but they are an essential part of your daily insulin resistance diet. They contain a good amount of low GI score carbohydrates. Whole grains are packed with fiber that helps prevent overeating by making you fuller with small portions.
The best types of wholegrain food are:
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Buckwheat
- Whole grain bread
- Bulgur
- Oatmeal
- Dry cereal
Switch to Lean Protein
Protein is the most vital part of your everyday meal. It helps stabilize blood sugar levels that prevent many diseases. Protein is also important for your mass muscle, especially if you incorporate exercise with their insulin resistance diet.
Incorporating the following lean protein into your diet is crucial for obtaining beneficial results:
- Chicken
- Fish
- Tuna
- Low fat cottage cheese
- Low fat cheese and deli meats
- Turkey
A general diet portion is equal to 1 cup low cottage cheese, 3 oz meat, or fish.
Beans
Beans are another excellent plant-based food full of fiber. Make you fuller with low Glycemic content and rich fiber nutrients.
Mostly all types of beans are suitable for insulin resistance diet such as:
- Peas
- Pinto
- Kidney beans
- Lima
- Red, white, and Black beans
- Chickpeas
- Lentil
Fiber Booster Intake
Fiber is an essential part of your food intake when it comes to stabilizing your blood sugar level. Unfortunately, most people don’t take enough fiber in their diet. An advised average intake of fiber for adults is 25 to 30 grams per day. However, the average intake among adults in the United States is 15 grams per day. Fiber-rich foods consist of carbohydrates that don’t get absorbed by the human body. As a result, they get processed slowly.
Fiber doesn’t raise sugar levels, make you feel fuller, prevent heart diseases and colon cancer. Foods that are rich in fiber include:
- Nuts and seeds
- Peas, beans, and pulses
- Wholegrain cereals, breakfasts, pasta, etc
- Apple, strawberry, & avocado, etc
- Potatoes with skin.
Bottom Line
Simple lifestyle changes such as eating right, exercising regularly and monitoring your weight can bring noticeable results. Consuming high amounts of carbohydrates can spike up the sugar level. Knowing your food and the right balance of good carbs per meal can help prevent any evaluation in diabetes and help to maintain weight as well.